What is RRBS?
Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing (RRBS) is a method to enrich for CpG-dense regions across the genome using enzymatic digestion of the input DNA before proceeding to the common steps in bisulfite sequencing library preparation such as bisulfite conversion.
Benefits of RRBS
-
RRBS reduces the number of required sequencing reads to achieve similar data quality compared to sequencing the entire bisulfite converted genome as in Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing (WGBS). It reveals DNA methylation information on important regulatory regions such as promoters and CpG islands, and in gene bodies. With approximately 10-20% of the sequencing reads that are normally required by WGBS, RRBS can cover ≥70% of promoters, CpG islands, and gene bodies, and around 35% of enhancers.
-
RRBS is more cost-effective compared to WGBS and is ideal for scientists to screen genome-wide DNA methylation information in large-scale studies.
Challenges of RRBS
-
RRBS targets CpG-rich regions such as promoters, CpG islands, and gene bodies but it only covers approximately 15% of the entire methylome. RRBS does not provide a comprehensive view of the methylation landscape, which can lead to missing important methylation information in regions that are not CpG-rich.
-
RRBS is not recommended for species with low CpG density due to the specific enzymatic digestion, which can lead to insufficient coverage and representation of the genome.
-
RRBS cannot distinguish between 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC).
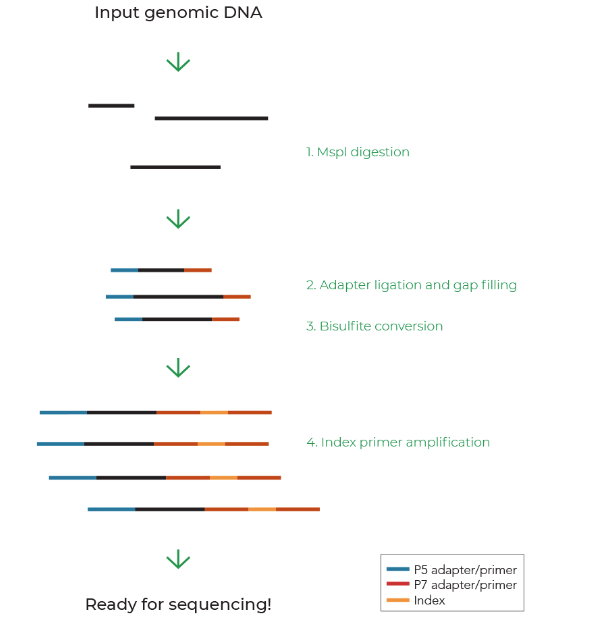
Many variations of RRBS have emerged over the years. An example of the basic RRBS workflow in Figure 1 covers the main steps to prepare RRBS libraries from input genomic DNA: MspI digestion, adapter ligation, bisulfite conversion, and PCR amplification with indexed primers. Zymo-Seq RRBS Library Kit has a simple protocol and is compatible with as low as 10 ng of genomic DNA, making RRBS more accessible to all users.1-4 Alternatively, consult with your dedicated genome-wide DNA methylation service provider to ensure you receive high-quality data5-6 from your precious samples.
Industry-Leading Solutions for DNA Methylation Studies
Zymo Research offers a comprehensive solution for DNA methylation profiling, streamlining your workflow from start to finish. Our industry-leading DNA purification technologies efficiently recover NGS-ready DNA from any sample type. This purified DNA seamlessly integrates with our bisulfite conversion and library preparation kits, simplifying your epigenomics research. Incorporating DNA methylation standards into your bisulfite sequencing workflow ensures precise validation of experimental conditions, delivering highly accurate and reliable NGS results. For labs looking to save time and resources, our Epigenome Sequencing Services offer a hassle-free way to uncover valuable insights from complex epigenetic patterns with ease.
With decades of experience in epigenetics, Zymo Research is uniquely positioned to support your projects using state-of-the-art products and services for DNA methylation analysis. From sample preparation to sequencing and reporting, Zymo Research scientists are available to support you every step of the way.
Citations
- Zhao, B.; van Bodegom, P. M.; Trimbos, K. B. Environmental DNA methylation of Lymnaea stagnalis varies with age and is hypermethylated compared to tissue DNA. Mol Ecol Resour 2023, 23 (1), 81-91.
- Venkatesh, G.; Tönges, S.; Hanna, K.; Ng, Y. L.; Whelan, R.; Andriantsoa, R.; Lingenberg, A.; Roy, S.; Nagarajan, S.; Fong, S.; et al. Context-dependent DNA methylation signatures in animal livestock. Environ Epigenet 2023, 9 (1), dvad001.
- Gurao, A.; Vasisth, R.; Singh, R.; Dige, M. S.; Vohra, V.; Mukesh, M.; Kumar, S.; Kataria, R. S. Identification of differential methylome signatures of white pigmented skin patches in Nili Ravi buffalo of India. Environ Mol Mutagen 2022, 63 (8-9), 408-417.
- Ben-Nun, O.; Kisliouk, T.; Marco, A.; Rosenberg, T.; Meiri, N. Early-life thermal stress mediates long-term alterations in hypothalamic microglia. Glia 2022, 70 (4), 619-633.
- Lu, Y., Brommer, B., Tian, X. et al. Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision. Nature 588, 124–129 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2975-4
- Von Walden, F., Rea, M., Mobley, C. B., Fondufe-Mittendorf, Y., McCarthy, J. J., Peterson, C. A., & Murach, K. A. (2020). The myonuclear DNA methylome in response to an acute hypertrophic stimulus. Epigenetics, 15(11), 1151–1162. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2020.1755581
